QGIS common errors and issues #
Here we are collecting common QGIS errors and issues as general QGIS training support.
Table of content #
Layers that should actually be in the same position are not on top of each other
Missing processing tools in the panels tool and incomplete vector tab
Coordinate systems: How do I redefine a dataset’s coordinate system?
Coordinate systems: Why is Mercator ever used if it’s so distorted?
Coordinate systems: My dataset is not located where it should be!
Coordinate systems: What coordinate system should my dataset be in?
Different QGIS versions#
The Wiki and in particular the videos in it are only a snapshot in time. QGIS itself, as well as the installable extensions, are constantly being developed and improved. Therefore there may be differences between the various versions in the appearance of the user interface or, in rare cases, even in the function. Consequently, there may be differences between the Wiki and the QGIS installed on your PC. Nonetheless this chapter focuses on common errors and issues, hopefully for many (upcoming) versions.
QGIS on Mac doesn’t open#
When opening QGIS for the first time on Mac you may get this error message:
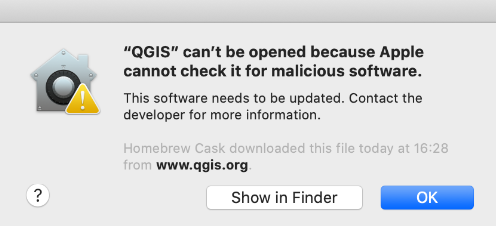
Fig. 41 Error when opening QGIS on Mac for the first time.#
To solve this, press the control button on your keyboard and right-click open.
If this problem persists, you can change the settings on your device. Go in the Settings > Security & Privacy and scroll down, click Open Anyway
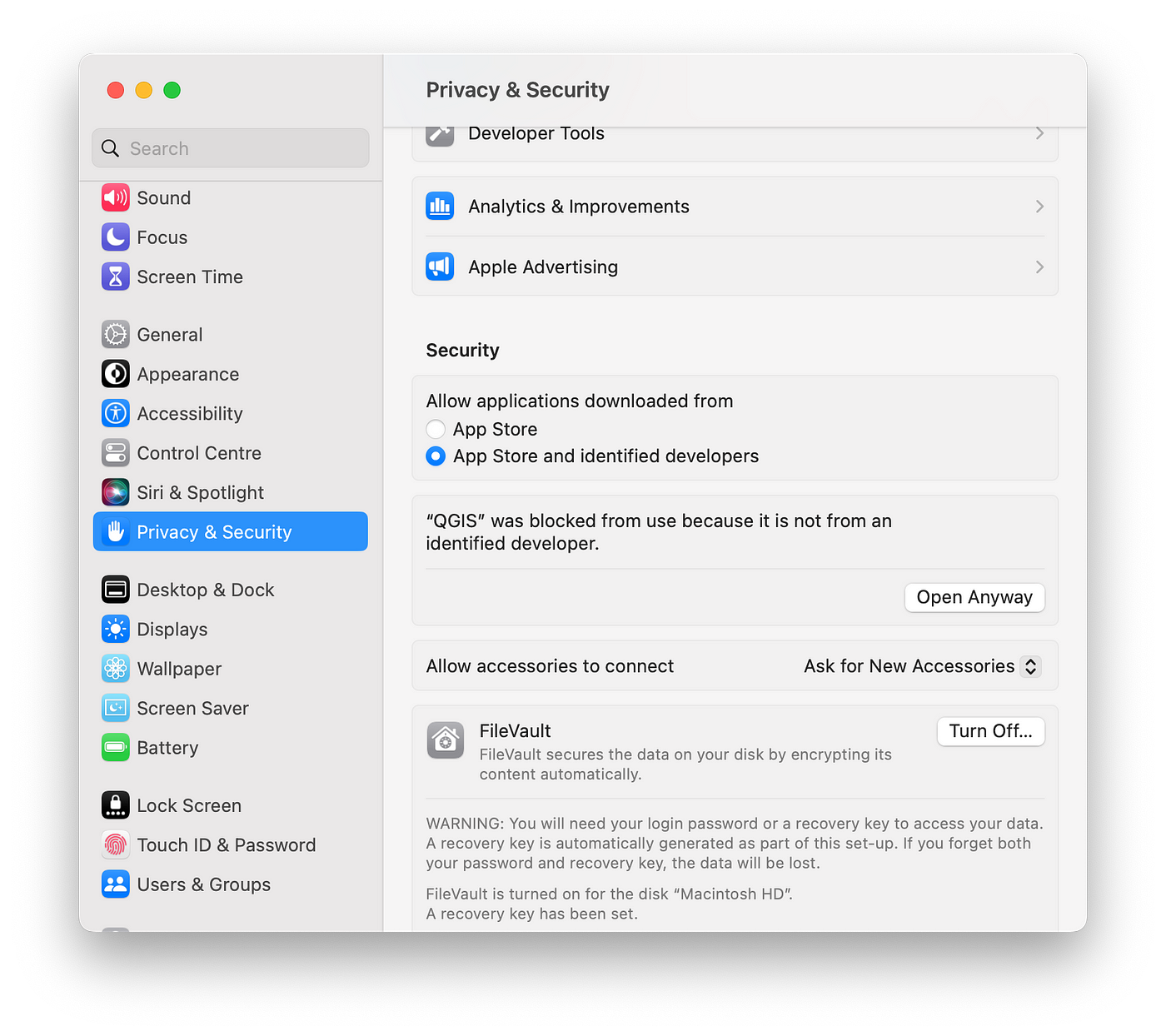
Fig. 42 Change settings to open QGIS on Mac.#
A layer is not displayed in QGIS#
Solution:
Right click on the corresponding layer.
Activate the
Zoom to Layerfunction in the pop-up window.
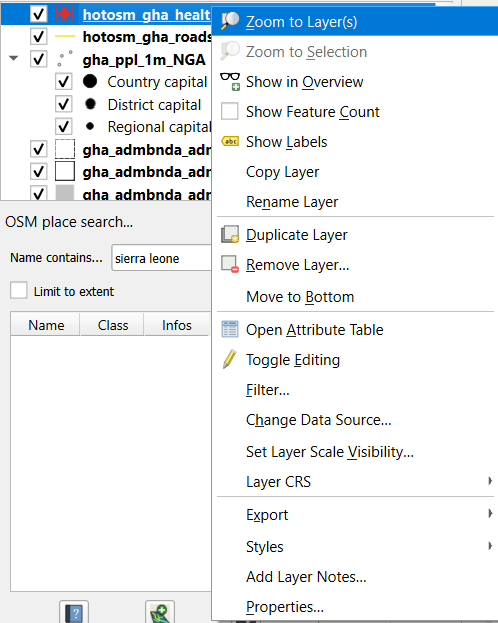
Fig. 43 Zoom to layer if layer is not displayed.#
A layer window has disappeared in QGIS#
Solution:
Open in the main tab
View.In the pop-up window select
Panels.In the sub-window hook the case
Layers.
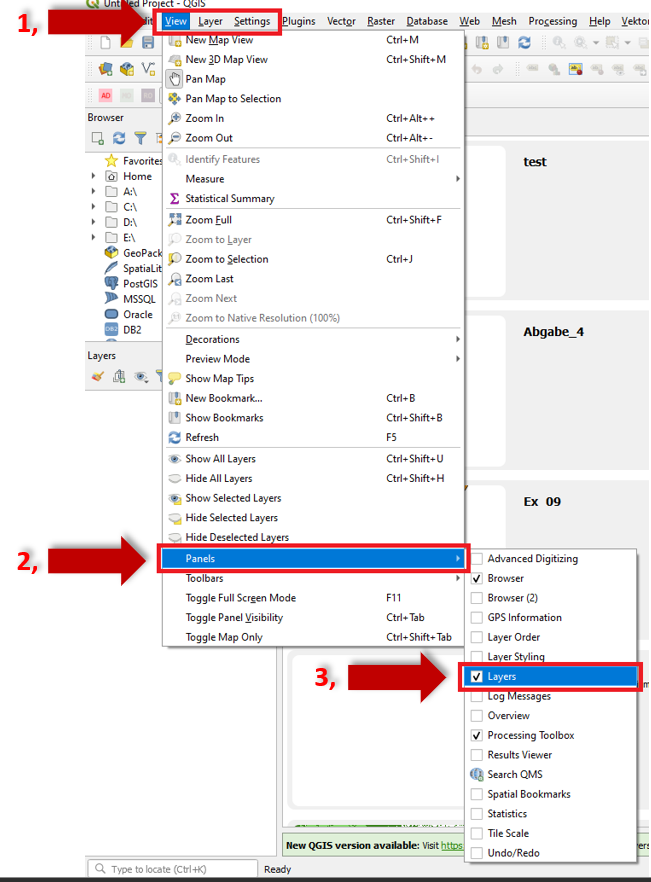
Fig. 44 Layer window disappeared.#
Layers that should actually be in the same position are not on top of each other#
Solution:
These sorts of problems are usually due to a) mismatching crs in layers and project, or b) an incorrect reprojection.
a)
Check the layer properties (right-click on the corresponding layer).
Select in the pop-up window
Properties.In the next pop-up-window select
Informationand check which projection is defined under the entryCoordinate Reference System (CRS).And additionally check if the same projection is set in the status bar at the bottom right.
Correct any discrepancies by reprojecting the layers or changing the setting of the crs project.
b)
Reprojecting:
When having two layers with different crs, then select one of the layers as the input layer having, f. e. the crs EPSG:32632 - WGS 84 and select EPSG:4326 - WGS 84 as the target crs. Start the algorithm and you will receive a new layer, identical to the input layer, but with a different crs.
It is displayed in the workspace in the same place as the other layers, as QGIS reprojects it at runtime. However, its actual coordinates are different.

Fig. 45 Layer with different crs.#
You can check this using the Add Geometry Attributes < Geometry Tools algorithm. The coordinates are different from the coordinates in the other two attribute tables of the other layers.
Instead do this:
Select the
Vectortab.Activate in the pop-up menu
Data Management Tools.And in the following pop-up menu
Reproject Layer.
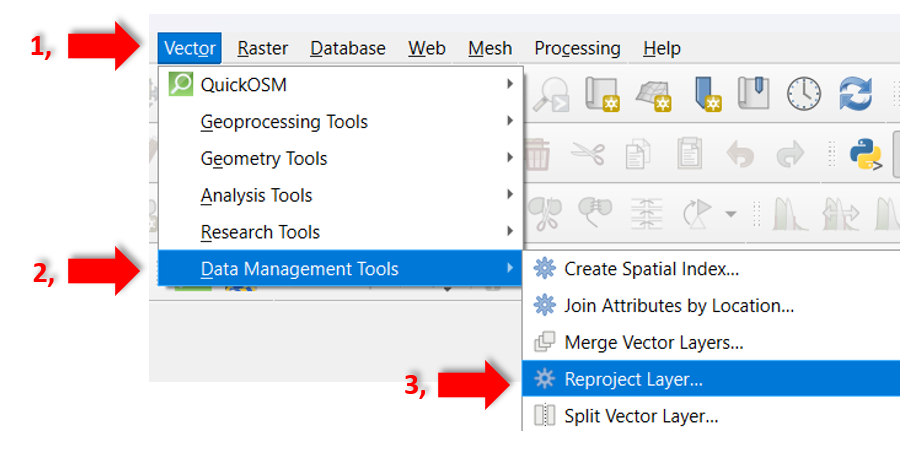
Fig. 46 Reproject Layer in QGIS.#
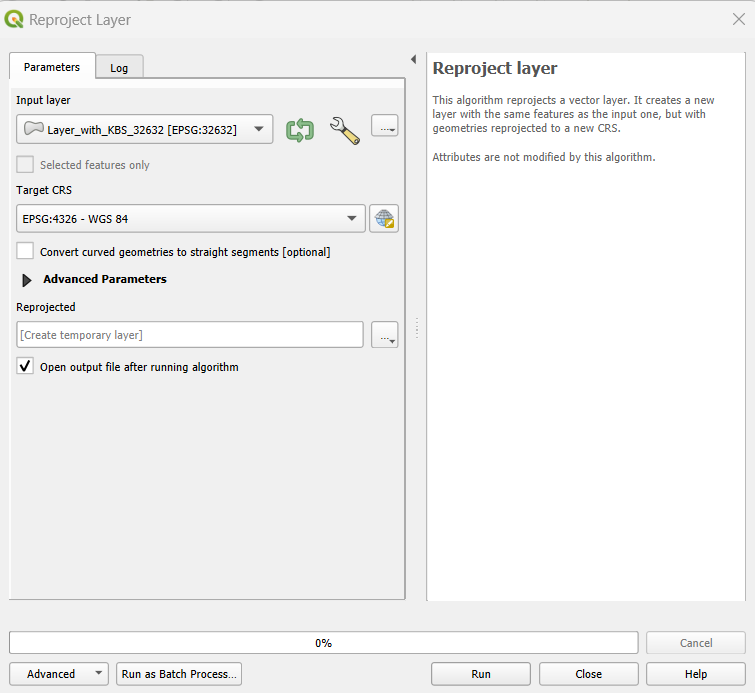
Fig. 47 Tool to reproject Layer in QGIS.#
Always save your reprojected layers by the Export and Save as functions because they are only temporarily saved and will disappear after closing the project.
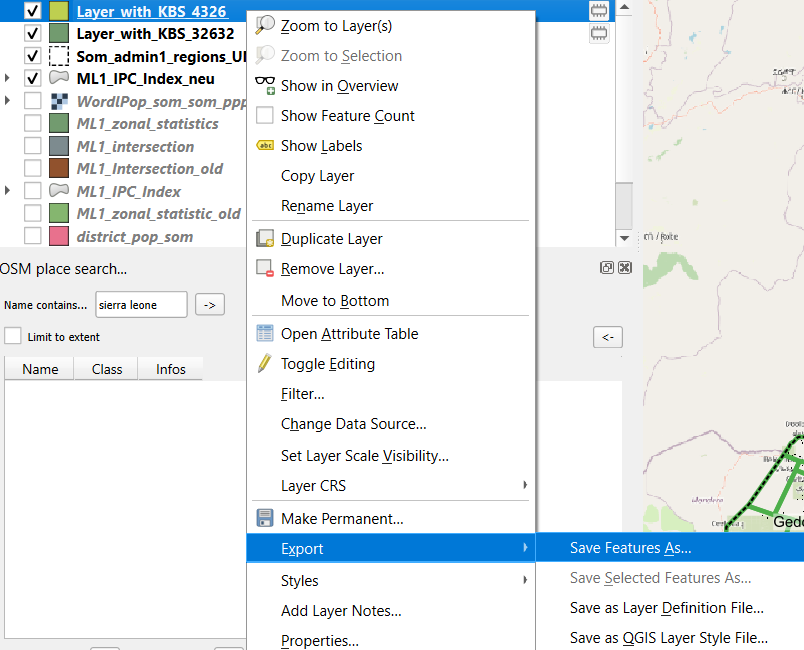
Fig. 48 Export reprojected layer.#
Similar procedure for raster layers …
Select the
Rastertab.Activate in the pop-up menu
Projections.And in the following pop-up menu
Warp (Reproject)
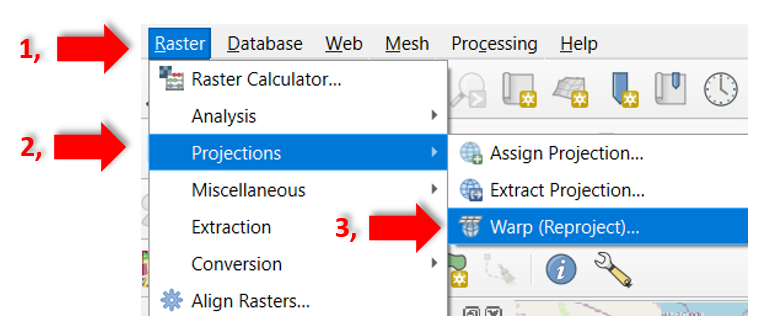
Fig. 49 Reproject raster layer in QGIS.#
Attention
Errors often occur if the crs is set and no reprojection tool has been used. If you suspect that your reprojection has gone wrong, delete all affected layers from QGIS, reload the data and then reproject and export them.
Layer file disappeared from the layer window#
If a layer file is no longer displayed or active in the layer window after reopening a QGIS project, it is only a temporary layer. Temporary layers have a symbol on the right of their name, as so:

Solution:
Next time, save it:
Click on the tab
Layerand onSave asin the pop-up window.
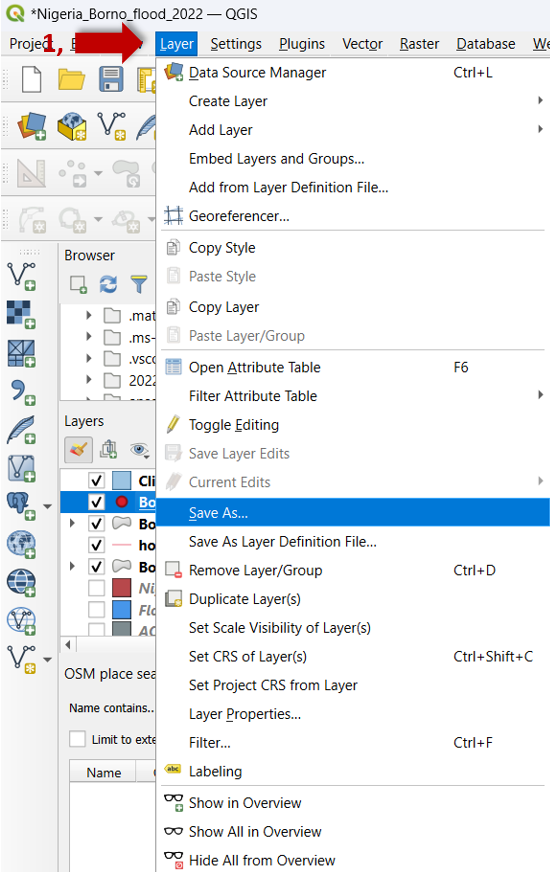
Fig. 50 Save layer.#
Put in a file name and click on the
three points to save the file in the chosen directory place.
to save the file in the chosen directory place.Select the corresponding CRS.
Click
ok.
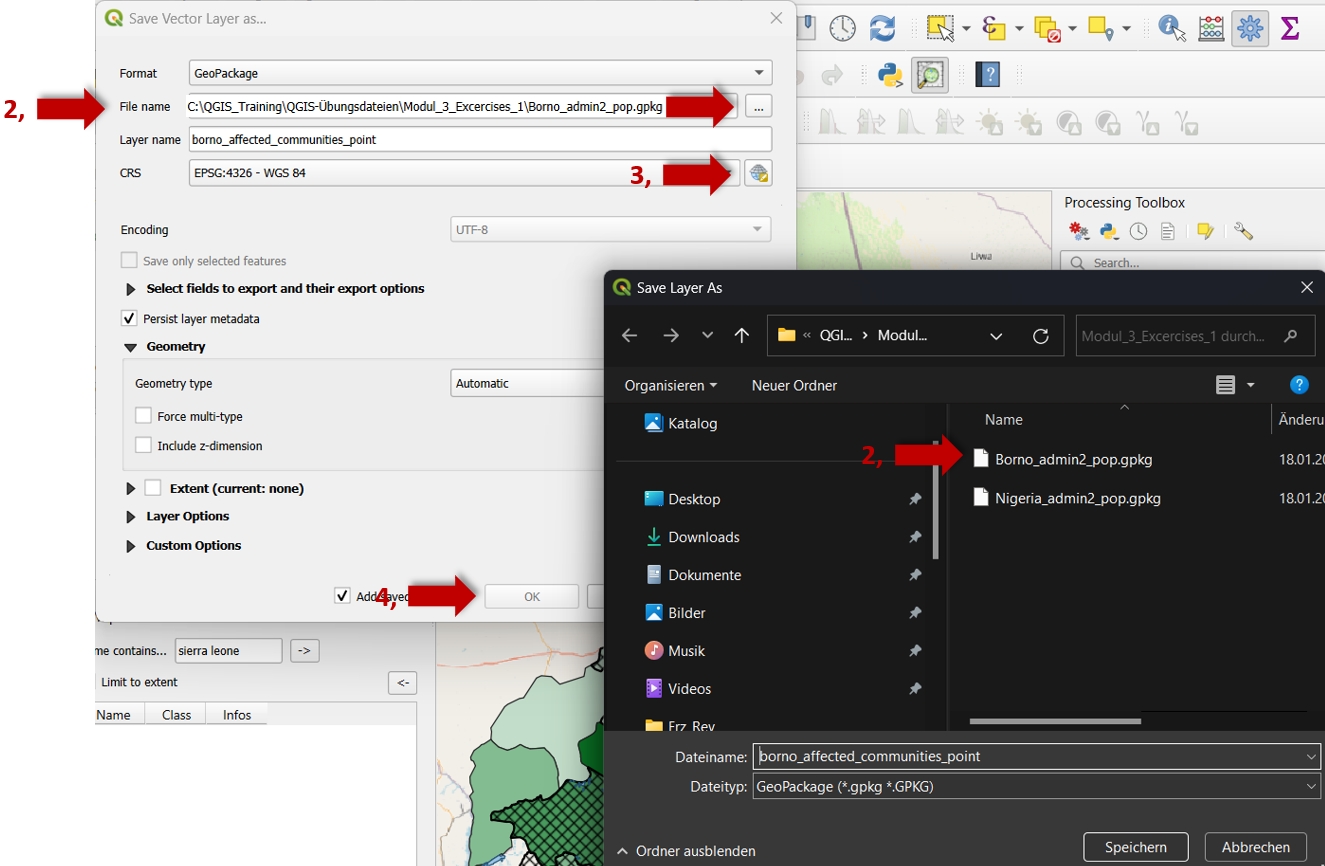
Fig. 51 Save layer in your directory.#
Missing processing tools in the panels tool and incomplete vector tab#
Solution:
Activate the
Processing Toolsby going toPlugins>Manage and install Plugins.Select
All.Rehook the
Processingfunction in the corresponding list.
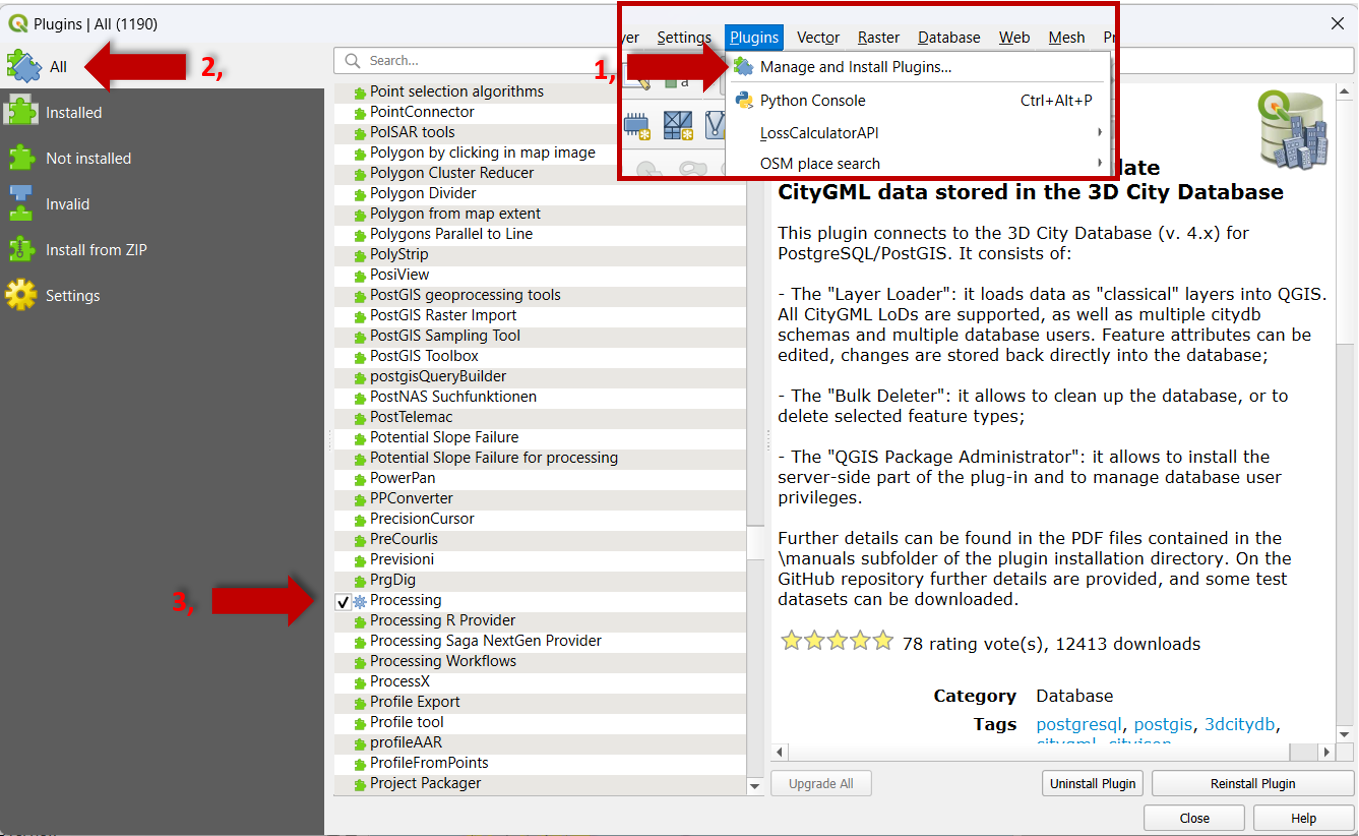
Fig. 52 Reinstall processing tool.#
See also: Geographic Information Systems https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/202111/missing-processing-tools-in-vector-menu-of-qgis
Missing toolbox#
Solution:
To reactivate the
Toolbox click on the
click on the View Tab.Select in the pop-up window
Panels.Set in the following pop-up window a hook for the
Processing Toolbox.
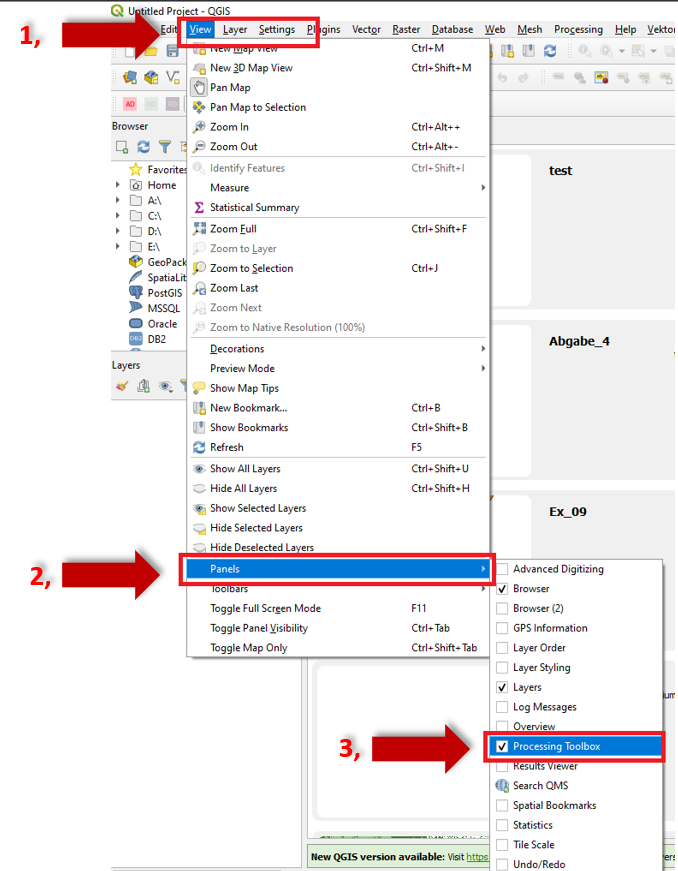
Fig. 53 Reactivate toolbox.#
The North arrow is not syncing with the corresponding map#
Solution:
There are two places where you have to define which map the north arrow should sync with.
In the Layout Tab (of the print layout) for the map image under General Settings make sure that the reference map has the right map selected.
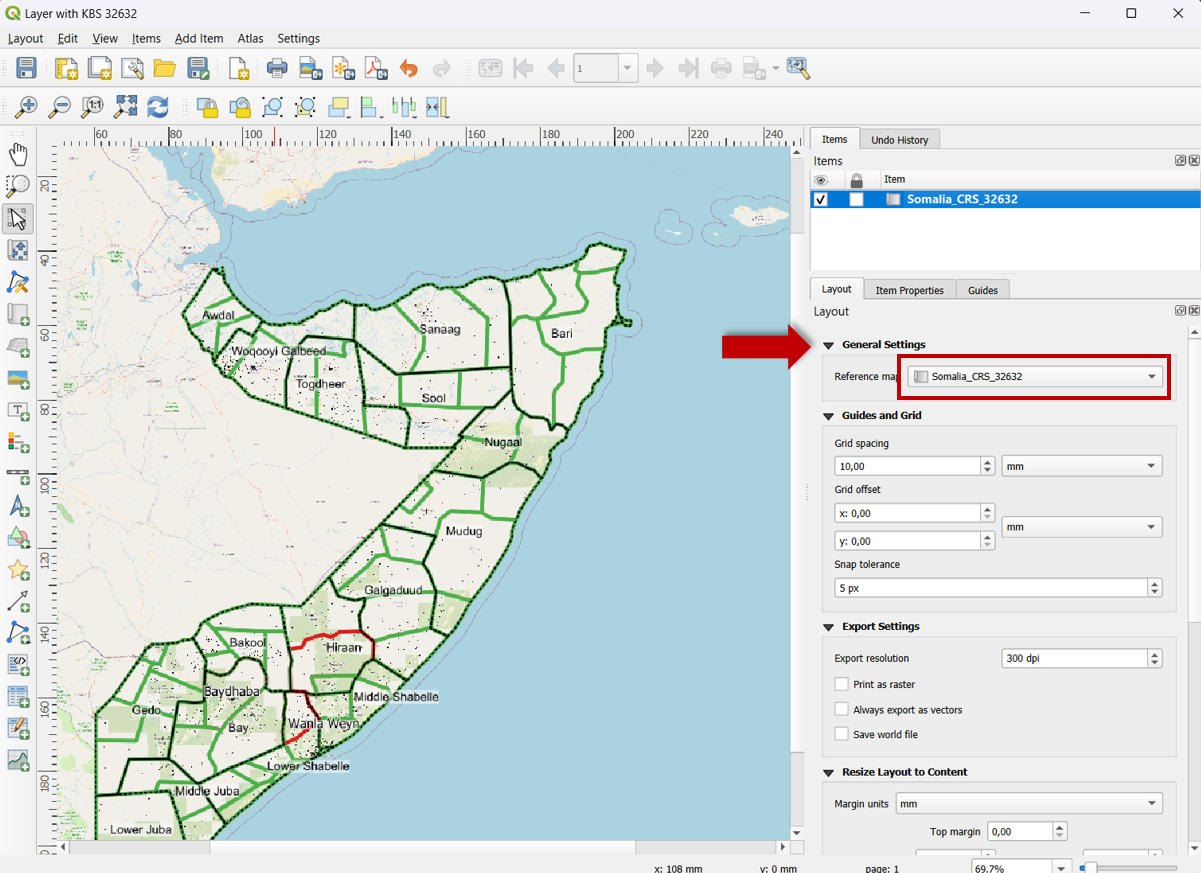
Fig. 54 Correct reference to map.#
See also: Geographic Information Systems https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/265095/north-arrow-not-syncing-with-map-qgis-2-18#:~:text=1 Answer&text=2-,There are TWO places where you have to tell it,and tell it which map
Invalid Geometry#
If the error message Invalid Geometries appears, it may be that vector files have “slipped” during the processing or downloading process (e.g. the lines of polygons no longer fit together exactly).
Solution:
These errors in the geometries can be corrected by running Fix Geometries. Search for it in the Processing Toolbox.
Coordinate systems: What do all these terms mean?#
Geospatial datasets consist of three basic data:
Attributes: the meanings or labels of a data point.
Coordinates: numbers describing the data point’s position in space.
Coordinate (reference) system: metadata describing the space itself: origin, axes, units, etc.
For example:
Attributes: “The White House” or “1600 Pennsylvania Avenue”
Coordinates: (-77.0367, 38.8976)
Coordinate (reference) system: WGS84 longitude,latitude
Tip
For further detailed information about coordinate systems have also a look at: https://ihatecoordinatesystems.com/#correct-crs
Coordinate systems: How do I redefine a dataset’s coordinate system?#
Redefining means the metadata about the coordinate system is modified but the coordinates are not. This contrasts with reprojections and transformations, which modify both the coordinate system and the coordinates.
Solutions:
In QGIS, for vector datasets, use the
Assign Projectiontool in theVector Generaltoolset, not theReproject Layertool. See also: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/user_manual/processing_algs/gdal/rasterprojections.html#assign-projectionIn QGIS, for raster datasets, use the
Assign Projectiontool in theGDALtoolset, not theWarp (Reproject)tool. See also: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/user_manual/processing_algs/gdal/rasterprojections.html#assign-projectionFrom the command line, for vector datasets, use
ogr2ogrwith the-a_srsparameter, not the-t_srsparameter. See also: https://gdal.org/programs/ogr2ogr.html#cmdoption-ogr2ogr-a_srsFrom the command line, for raster datasets, use
gdal_editwith the-a_srsparameter. See also: https://gdal.org/programs/gdal_edit.html#cmdoption-a_srs.py
Coordinate systems: Why is Mercator ever used if it’s so distorted?#
Mercator is the only conformal cylindrical map projection. Cylindrical map projections mean the whole earth fits into a rectangle, which is very convenient for data processing algorithms that are used to working with rectangular images. Conformal means that angles and shapes are always preserved: north is always up, squares are always square, etc.. Using a non-conformal projection would make things look stretched, squashed, and/or rotated when zooming in.
Fig. 55 Mercator projection.#
Mercator does enlarge areas farther from the equator, but at least this distortion is the same horizontally and vertically. And it’s trivial to calculate a scale factor to correct measurements (See also: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mercator_projection#Scale_factor).
The only time the distortion is problematic is when viewing a global-scale map with a range of different scale factors, but most maps are not global-scale and there are plenty of better projections to use for this case.
Coordinate systems: My dataset is not located where it should be!#
Your dataset probably has the wrong coordinate system. This is the more general case of the previous problem. This can happen if the coordinate system is missing altogether, in which case GIS software often assumes that it is the same coordinate system as a previously loaded dataset, or the coordinate system set in the “project” or “map document”.
Solution:
Redefine the coordinate system, redefine i.e. change the coordinate system but not the coordinates, to the correct coordinate system.
Open your
Project: Open the QGIS project where you want to redefine the coordinate system.Access
Project Properties: Go to theProject menuat the top of the QGIS window and selectProperties. Alternatively, you can pressCtrl + Shift + Pas a shortcut.Coordinate System Tab: In the
Project Propertieswindow, select the `Coordinate System tab.Change Coordinate System: Here, you can select a new coordinate system for your project. You can search for a specific coordinate system using the search bar, or you can browse through the list of available coordinate systems.
Apply Changes: Once you’ve selected the desired coordinate system, click OK to apply the changes. QGIS will reproject the layers in your project to match the new coordinate system.
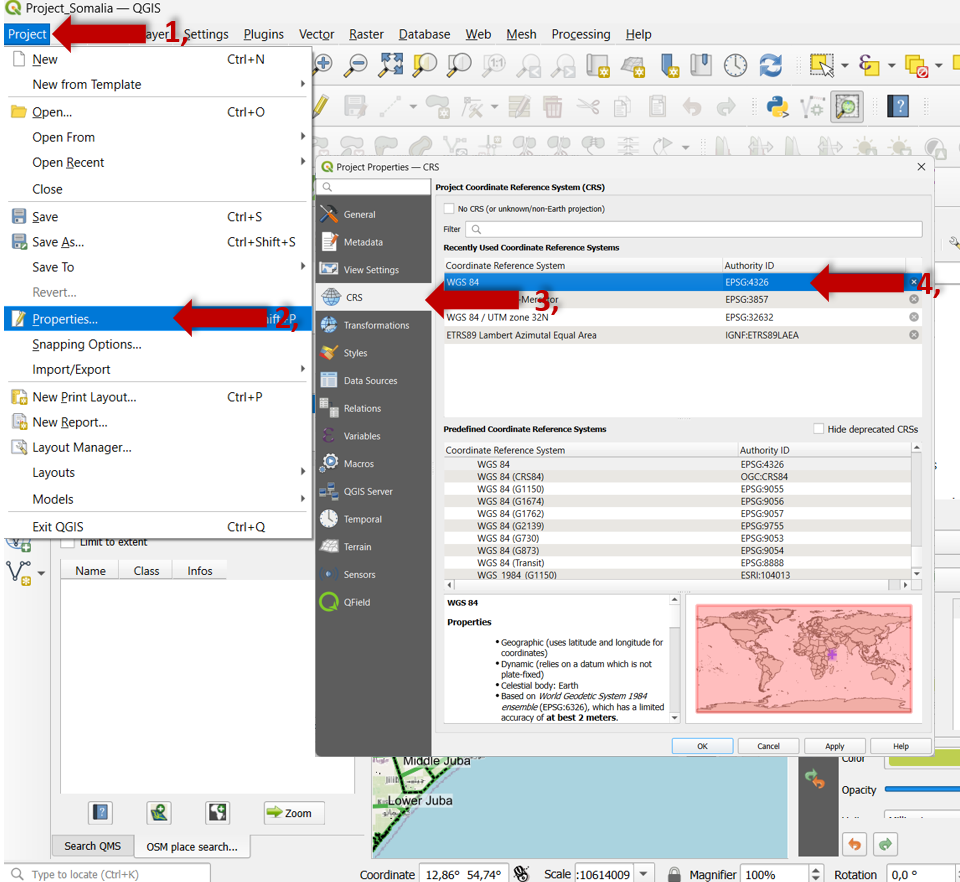
Fig. 56 Redefining CRS.#
Check and Adjust Layers: After redefining the coordinate system, it’s essential to check your layers to ensure they align correctly. Some layers may require manual adjustments or reprojection if they don’t align as expected. And have also a final look at the right bottom of the QGIS window where the actual CRS is indicated.
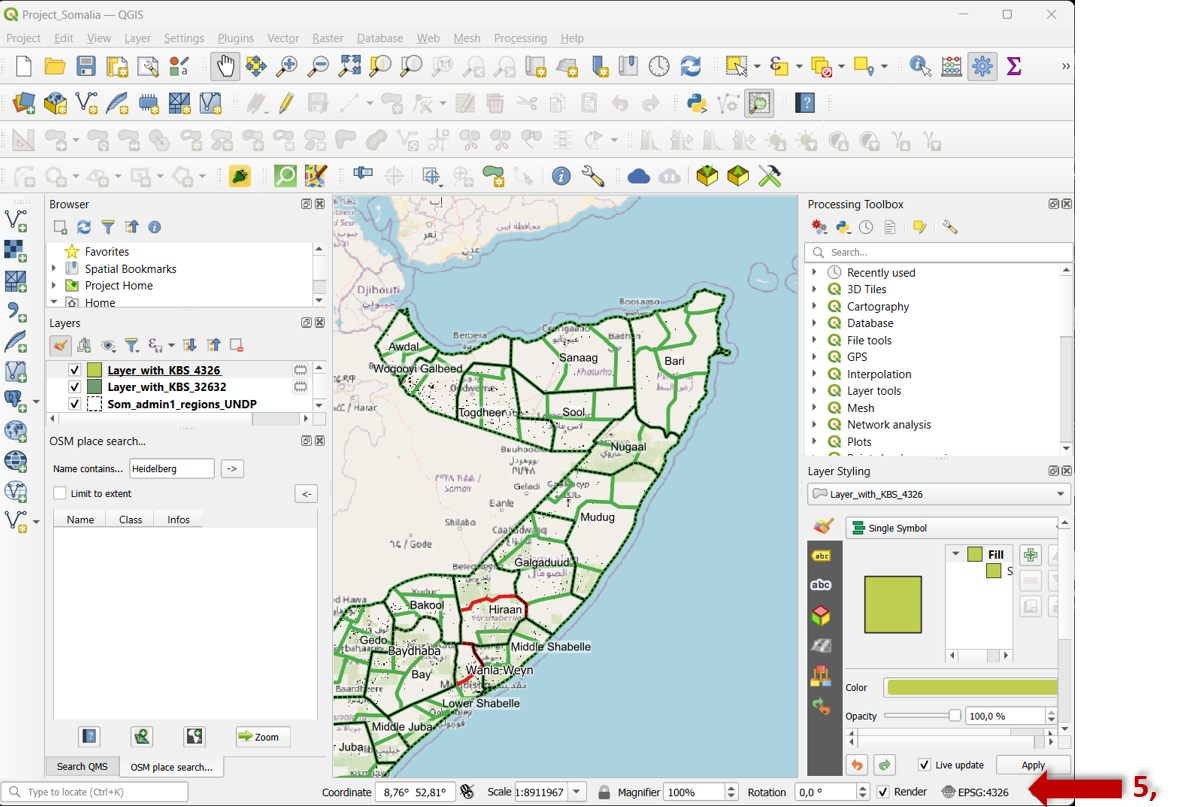
Fig. 57 Check redefining CRS.#
Coordinate systems: What coordinate system should my dataset be in?#
A data point’s attributes give context to where on the earth it is located. Most GIS software will display the minimum and maximum coordinates in the layer’s properties as “extent” or “bounding box”.
Solutions:
If the attributes indicate the approximate longitude,latitude where the coordinates should be located, try doing a reverse lookup. This iterates over every well-defined coordinate system, unprojects the X,Y coordinates to WGS84, and measures the error to the known longitude,latitude. Errors less than a few hundred meters denote a reasonable projection, though this isn’t precise enough to determine the GCS. You can run this sample code yourself, or use this form:
If the coordinates have X-values between -180 and 180, and Y-values between -90 and 90, then you probably want to redefine a geographic (with longitude and latitude) geographic coordinate system (GCS) like WGS84.
If the coordinates have large absolute values, try redefining them to a local coordinate system like UTM, Gauss-Krüger, State Plane, or a national grid. Also consider trying neighboring zones, e.g. if UTM Zone 19N is wrong, try UTM Zone 18N.
If the attributes suggest the dataset is in the USA, then there might be a problem converting to/from Freedom Units. Try multiplying/dividing a data point’s coordinates by 3.28084 to convert feet to meters/meters to feet and see if that places it in the proper location.
If the minimum X/Y coordinates are both zero and the maximum X/Y coordinates are both positive, then the dataset may have been exported from non-geospatial software like Photoshop or Illustrator or Inkscape. This is especially likely if the dataset is flipped vertically since those editors typically have the Y-axis increasingly going down. You will need to manually georeference the dataset to use it, which changes both the coordinates and the coordinate system.
See also the following Wiki_Page Projections.
My dataset is slightly offset from where it should be!#
Your dataset probably has the wrong longitude/latitude geographic coordinate system (GCS). Different GCSs define slightly different sizes/shapes of the Earth (their ellipsoids) and different positionings on the Earth (their datums). As a result, the same longitude/latitude coordinates in two different GCSs can appear offset, although typically within tens of meters of each other. This can happen even if you are using a projected coordinate system (PCS) whose units are not degrees of longitude/latitude since PCSs have a GCS embedded within them.
Fig. 58 Offset because of wrong GCS. Source: Dan Mahr. All rights reserved. This content is excluded from our Creative Commons license.#
Solution:
Redefine the coordinate system, i.e. change the coordinate system but not the coordinates, to one of the following:
Try to redefine to the WGS84 GCS.
If your dataset was collected with GPS, try redefining it to WGS84.
If your dataset was collected with GLONASS, try redefining it to PZ-90.
If your dataset was collected with Galileo, try redefining it to ITRF.
If your dataset is in the USA, try redefining it to NAD27, NAD83, or WGS84.
If your dataset is in Europe, try redefining it to ED50, ETRS89, or WGS84.
If your dataset is in Australia, try redefining it to GDA94 or GDA2020.
If your dataset is in China and/or collected with BeiDou, good luck. :weary:
Wrong data results or missing data#
When you get wrong data results or missing data, please check your file names. You should not use file names with capitals, special characters or empty spaces. Always use underscores between the words for the file name.
File Management Issues#
There may be different reasons, e.g. reopening your QGIS project, not all files will be displayed correctly because some got lost or were stored in different places. In any case, there is a solution: a clear folder structure.
Solution:
Recommended standard folder structure:
Fig. 59 Standard folder structure. Source: HeiGIT#
How it might look like on your pc:
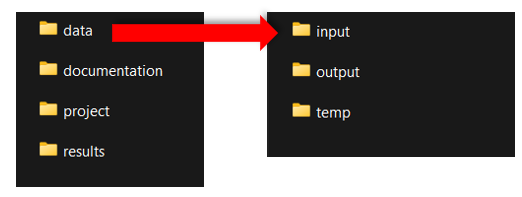
Fig. 60 Standard folder structure on your PC.#
The standard folder structure has two principal advantages:
By sharing the whole project folder, we can be certain that the project will run without problems on a different computer.
The folder structure supports the proper organization of geodata and supports the stable function of a QGIS project.
The folder structure template can be downloaded here.
Tip
The layer data used in the project are not saved in the project file. Instead, the project file only contains the file paths where the layer data were located at the time the project was last saved on the PC. If the location of this layer data is subsequently changed, the error message “handle unavailable layers” will appear when the project is opened again. Good data organisation with a fixed and well thought-out folder structure prevents such problems.
See also the following Wiki_Page for How to create a new QGIS project and How to open an existing QGIS project.
Specific QGIS problems#
Basic settings > Deactivating the automatic projection selection#
After installing QGIS, some basic settings should be changed to avoid possible sources of error. If a layer file does not have a projection, a projection must be defined for it when it is imported into QGIS. By deactivating the automatic projection selection, this projection can be defined manually. This prevents layers from accidentally being in the wrong projection.
Select the
Settingstab.Then activate in the navigation menu
Options.In the pop-up window select
CRS Handling.Under
CRS for projectsactivateUse CRS from first layer added.And under
CRS for layersactivatePrompt for CRS.
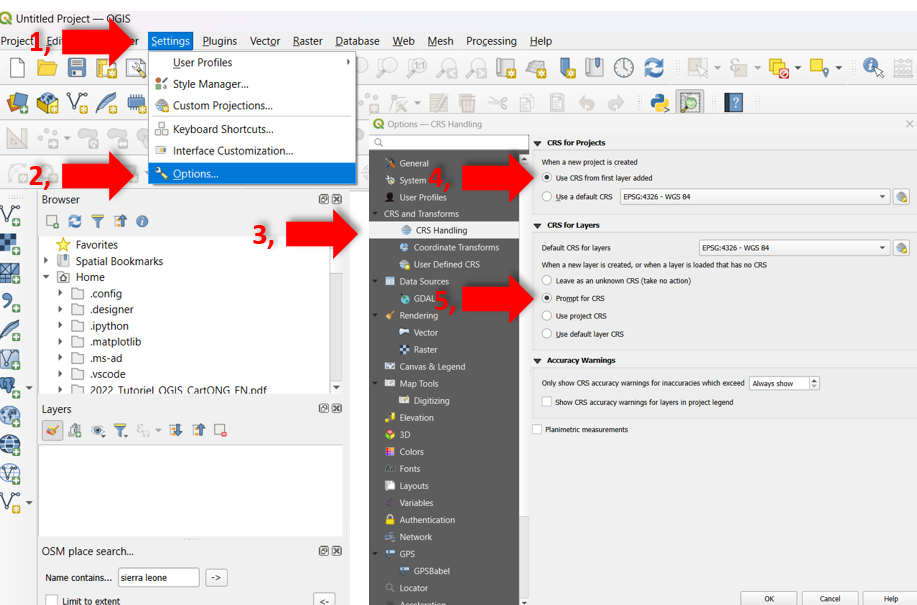
Fig. 61 Change crs settings in QGIS.#
Saving regularly#
Unfortunately, GIS programs are notorious for freezing or crashing completely. Although there is a trend towards fewer complications with better hardware, even a “gaming PC” costing several thousand dollars is not completely safe. More complex tasks with longer calculation times may still cause problems. Regular saving is therefore recommended.
See also the following Wiki_Page Save and open QGIS Projects.
GRASS applications#
QGIS also allows the use of tools from external GIS software, such as GRASS GIS. GRASS does not have to be downloaded separately, but is automatically installed when QGIS is installed. GRASS tools are identified by their icon.
Attention
Please note that the GRASS software is not started when the standard QGIS application is started. Consequently, an error message may appear when using GRASS tools. This can be remedied by opening the QGIS with GRASS application (found via the computer’s search function) instead of the standard application.
SAGA with Linux#
SAGA is another external GIS software. SAGA tools are identified by their icon. When using Windows or MacOS as the operating system, SAGA is automatically implemented when QGIS is installed. With Linux, however, SAGA is not installed automatically and must be installed manually. Experience has shown that this installation is not always easy and can cause problems. Alternatively, you can either use a Windows or MacOS virtual box or refrain from using SAGA tools (you will then have to search for alternative tools yourself).
Umlauts, special characters, spaces in file paths#
If the file path contains umlauts (ä,ö,ü), special characters (!,?, ., etc.) or spaces, this can lead to problems when these files are processed by QGIS. It is therefore recommended that you avoid these characters in your file paths (write out umlauts, replace spaces with _).
Attention
Temporary files are user-specific (if several people use one PC, each person has their own temporary files). The file path therefore contains your user name. If this contains problematic characters, it may therefore be advisable to change it.
QGIS Help Access Links#
Here you will find further help access links or QGIS community/forum links to address specific issues:
QGIS tutorials and tips:#
Collection of QGIS tutorials and tips: https://www.qgistutorials.com/en/
QGIS training manual: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/training_manual/index.html
QGIS user guide: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/user_manual/index.html
QGIS server guide/manual: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/server_manual/index.html
QGIS plugin user manual: https://docs.qgis.org/3.28/en/docs/user_manual/plugins/plugins.html
QGIS workshop and video tutorials (Harvard University): https://gis.harvard.edu/qgis-workshop-and-video-tutorials-0
QGIS tutorial (CartONG): https://cartong.pages.gitlab.cartong.org/learning-corner/en/6_tutorials/6_3_gis/6_3_1_qgis
QGIS community/forums:#
Geographic Information Systems: https://gis.stackexchange.com/?tags=qgis
QGIS user groups: https://www.qgis.org/en/site/forusers/usergroups.html#qgis-usergroups
QGIS YouTube channels:#
The best YouTube channels in QGIS and open source gis tools: https://hatarilabs.com/ih-en/the-best-youtube-channels-in-qgis-and-open-source-gis-tools-in-any-language
Absolute beginners guide to QGIS: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NHolzMgaqwE
QGIS complete tutorial for beginners: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d15Xl4OphDk
QGIS for beginners: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Eg4_duqH5Q4
Introduction to QGIS: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kxJI5FAGjzQ
ChatGPT#
And don’t forget ChatGPT https://chat.openai.com/ It is quick!