🚧 This training platform and the entire content is under ⚠️construction⚠️ and may not be shared or published! 🚧
9.1. Spatial Network Analysis Theory#
9.1.1. Understanding Networks: Analysis and Insights#
Networks serve as simplified representations of real-world systems. A network comprises nodes and edges, representing entities and their relationships respectively. Rather than being defined by coordinates, positions within a network are determined by connectivity. In GIS (Geographic Information Systems), networks play integral roles in transportation modeling and supply chain networks such as water and energy distribution. Additionally, they are utilized for analyzing the service areas of healthcare facilities. For instance, analyses can assess areas vulnerable to flooding to ascertain the potential impact on healthcare services during a disaster.
9.1.1.1. Components of a Graph#
Creating a graph involves defining its nodes (vertices) and edges (connections between nodes).
Defining Nodes: entities, objects, locations → Features in OpenStreetMap (hospitals, schools etc.)
Identifying Edges: roads or pathways between locations → Ways in OpenStreetMap (roads, paths, cycleways)
Additional Information Edges can be endowed with diverse weights. OpenStreetMap features tags such as road type, segment length, speed limit, and surface condition, which can be interpreted as weight attributes. Depending on your requirements, you can compute the shortest route or opt for the route with minimal elevation gain.
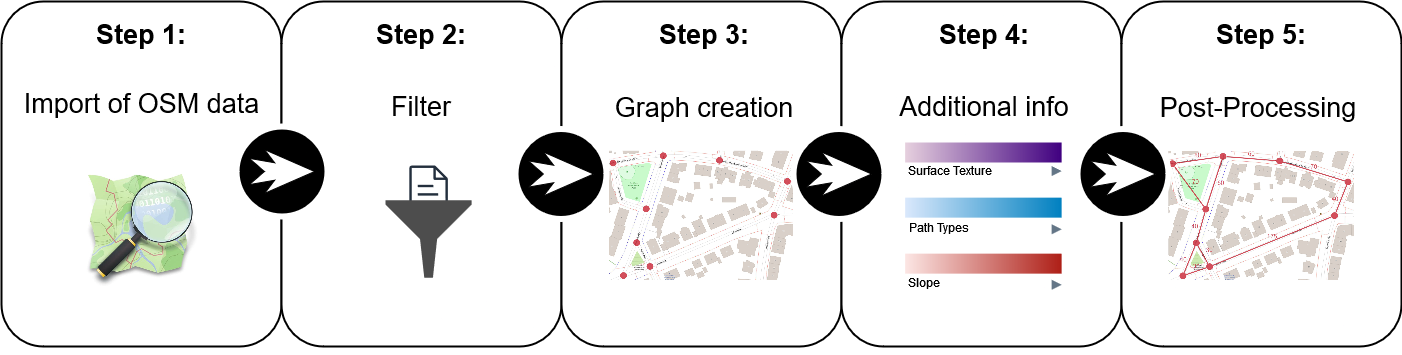
Fig. 9.1 Visualization depicting the conversion process from OpenStreetMap (OSM) geodata to a graph representation. Source: HeiGIT#
9.1.1.2. Dijkstra Algorithm#
E. W. Dijkstra
Discovered 1956, published 1959
Single pair shortest path algorithm (SPSP) - for directions / A → B routing
Single source shortest path algorithm (SSSP) - for isochrones
Base of a multitude of routing algorithms

Fig. 9.2 The GIF illustrates the step-by-step process of determining the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in a graph. As the algorithm progresses, nodes are visited and the shortest distances from the source node are continuously updated until all accessible nodes have been explored. Source: HeiGIT#
9.1.1.3. Analysis#
You can determine directions or standard routes, which unveil the shortest path between two points. Isochrones offer insight into the area accessible within a specified time or distance threshold. Additionally, generating a matrix enables the assessment of time or distance between predefined locations. Alternatively, graphs facilitate travel optimization by computing the most efficient sequence for visiting a given set of points.
9.1.1.4. Openrouteservice#
9.1.1.4.1. General Information#
Graphhopper based routing machine since 2008
Completely Open-Source
Global public API
updates every week
more than 100GB RAM per routing profile
some limitations due to computational capacities
Can also run on your local laptop
a small to medium country with one profile
freedom of choice on limitations
Different routing profiles (car, hgv, bike, pedestrian, wheelchair)
9.1.1.4.2. Services#
Directions/standard routing: Shortest path between two locations
Isochrones: Area reachable within a limit (time | distance)
Matrix: Times / Distances between a set of locations
Optimization: Best order to visit a set of points
This module provides an accessibility analysis based on Openrouteservice isochrones.
9.1.1.4.3. Isochrones#
Different profiles: car, pedestrian, bike, heavy goods vehicles (HGV)
Avoid areas, avoid, road types
Further dynamic preferences: green routing, noise aware routing, landmark routing, (heat aware routing)
Based on profile and preferences what area is reachable within a given time limit?
Determine: reachability, catchment areas
Max. 60minutes on the public API
SDKs & Plugins: Python, R, JavaScript, QGIS Plugin “ORS Tools”
For more information click here: [https://openrouteservice.org/]