Accessibility to healthcare#
Using GIS isochrones methods, healthcare facilities catchment areas can be assessed to determine accessibility and service coverage. By analyzing spatial data and travel times, isochrones help identify the population that can reasonably access these facilities, aiding in planning and resource allocation for improved healthcare access. This approach can supports policymakers and healthcare administrators in optimizing facility placement and addressing underserved areas.
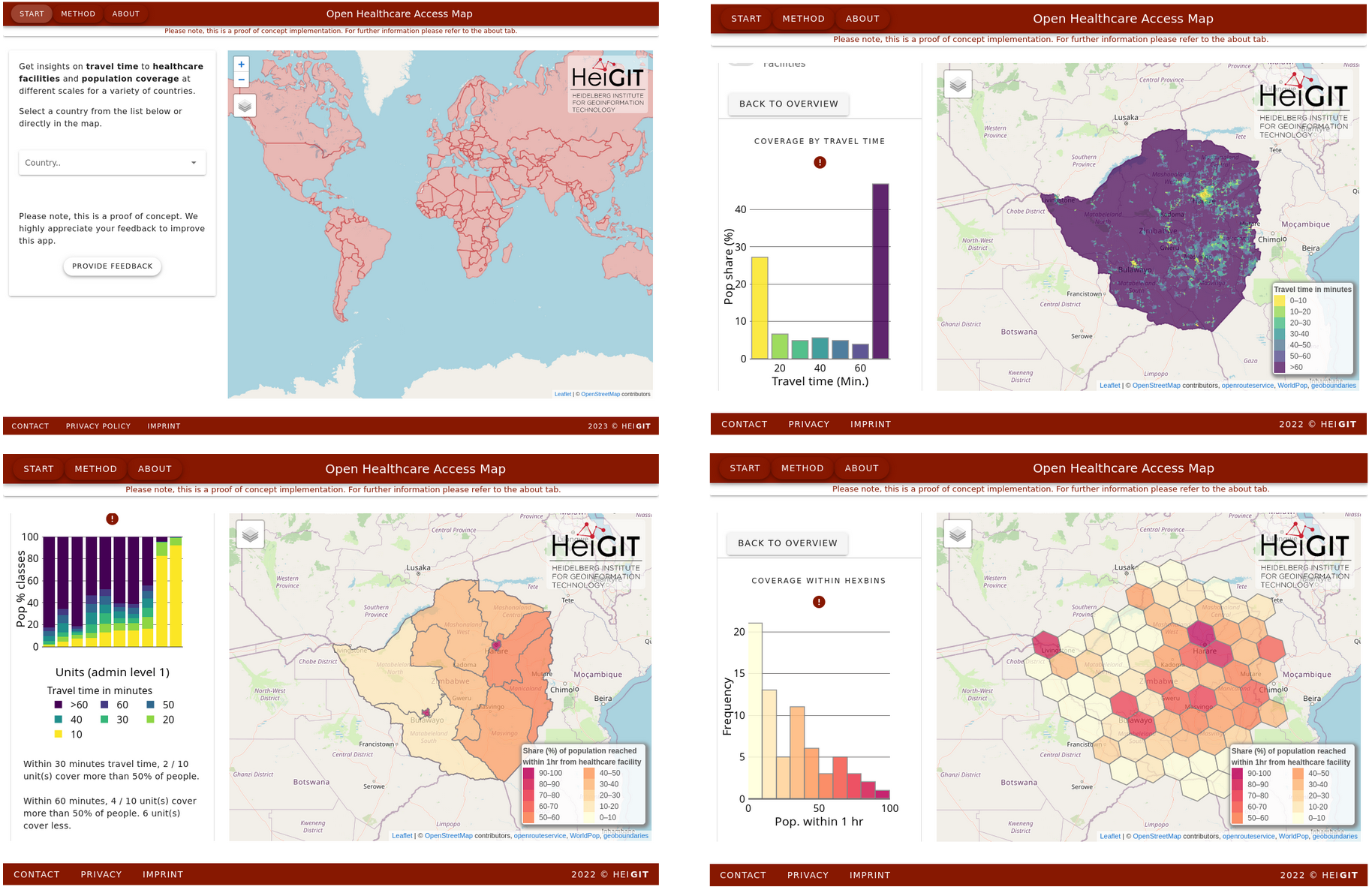
At HeiGIT we created a global visualization of healthcare accessibility based on OpenStreetMap facilities and openrouteservice Isochrones.
Isochrone based accessibility towards healthcare facilities
Differentiated by facility type
primary care
secondary care
Globally available
Different scale per countries:
Admin 1, 2
Hexagons (ISEA3H level 8)
https://apps.heigit.org/healthcare_access/#/
Example Kosovo
https://apps.heigit.org/healthcare_access/#/countries/xkx
References:
Geldsetzer, P.; Reinmuth, M.; Ouma, P. O., Lautenbach, S.; Okiro E. A.; Bärnighausen, T.; Zipf, A. Mapping physical access to health care for older adults in sub-Saharan Africa and implications for the COVID-19 response: a cross-sectional analysis. The Lancet Healthy Longevity. 2020;1(1):e32-e42. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-7568(20)30010-6))
Petricola, S., Reinmuth, M., Lautenbach, S. et al. Assessing road criticality and loss of healthcare accessibility during floods: the case of Cyclone Idai, Mozambique 2019. Int J Health Geogr 21, 14 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12942-022-00315-2
Klipper, I. G., Zipf, A., and Lautenbach, S.: Flood Impact Assessment on Road Network and Healthcare Access at the example of Jakarta, Indonesia, AGILE GIScience Ser., 2, 4, , 2021. https://doi.org/10.5194/agile-giss-2-4-2021
